Key Takeaways
- Heat pumps offer an energy-efficient alternative to traditional HVAC systems.
- Recent technological advancements allow heat pumps to operate reliably in various climates.
- Upgrading a modern heat pump system can significantly reduce energy bills and carbon emissions.
- Proper sizing, installation, and maintenance are critical to maximizing efficiency and lifespan.
- Multiple types of heat pumps are available to fit different home layouts and requirements.
- Consumer incentives and rebates may offset initial installation costs.
The Rise Of Heat Pumps For Everyday Homes
More households search for solutions that provide year-round comfort without breaking the bank or harming the planet. Advances in HVAC technology have put heat pumps in the spotlight, as they offer remarkable versatility by efficiently handling heating and cooling tasks. Unlike traditional systems that burn fuel or rely solely on electric resistance, heat pumps draw on the principles of thermodynamics, moving rather than creating heat. This breakthrough is why modern air conditioner heat pump units have captured the attention of energy-conscious consumers and builders focused on future-proofing new homes.
With the need for climate solutions increasing, the trend is clear: homeowners value systems that lower monthly costs while benefiting the environment. The U.S. Department of Energy has reported that heat pumps use far less electricity than their resistance heating counterparts, transferring up to three times more thermal energy than they consume. Neighbors are starting to compare energy statements, with those using heat pumps often surprised by the reduction in their utility bills, sometimes as much as 50%. It’s not just about saving on costs; it’s a growing awareness of the ecological impact that home energy choices can make.
How Heat Pumps Work In All Climates
Conventional wisdom once claimed heat pumps were best suited for temperate regions. However, the latest technological advancements, such as enhanced scroll compressors, highly efficient refrigerants, and defrost cycles, have redefined their operational range. Today, superior heat pumps can comfortably heat homes when outdoor temperatures dip below freezing. This innovation is a game-changer for families in regions known for snowy winters. States previously limited to gas or oil heating, like Maine or North Dakota, now witness broad heat pump adoption. The capability to extract and transfer ambient heat—even in challenging weather—makes these systems appealing across the map.
Firsthand accounts from homeowners living through harsh winters demonstrate that systems maintain steady indoor temperatures while dramatically lowering heating costs. For many, the backup furnace rarely kicks in anymore. In addition to consistent warmth, users notice that air flows remain fresher and humidity is more controlled, improving indoor air quality and day-to-day comfort. These benefits help to dispel outdated myths and expand the reach of heat pumps as a viable, dependable choice in every region.
Types Of Heat Pumps And Their Features
Finding the right heat pump requires a closer look at a home’s needs, construction, and the expected climate. The market offers several options:
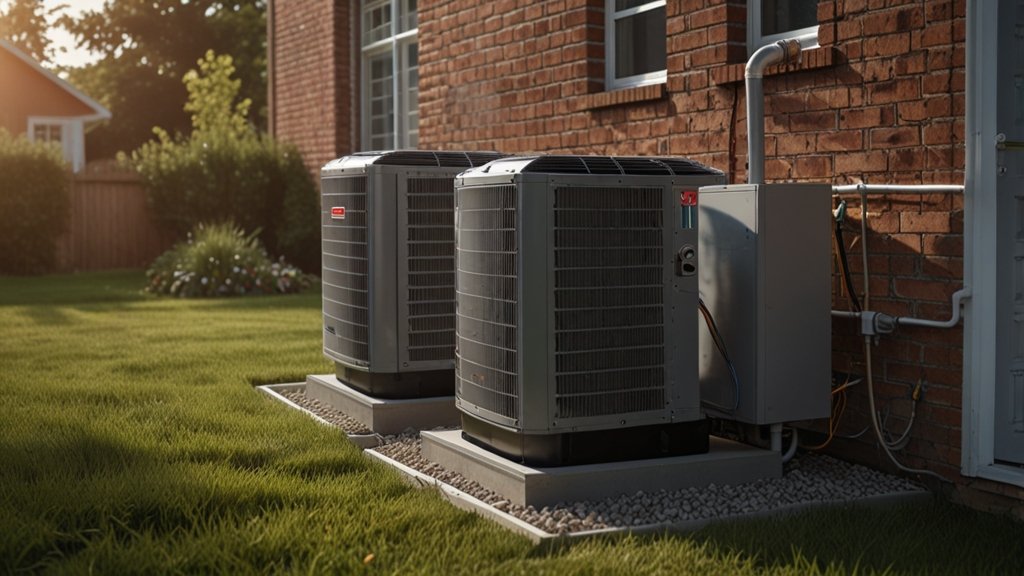
- Air-source heat pumps: The most widely used solution in residential settings, air-source models efficiently transfer heat between the inside and outside air, offering heating and cooling. They fit well into most retrofit and new construction scenarios, and recent advancements allow them to function even on bitterly cold days.
- Ground-source (Geothermal) heat pumps harness the consistent temperature below the earth’s surface, leading to extremely high efficiency rates. Although initial installation requires a bigger investment and enough land for underground loops, homeowners are often rewarded with impressively low operational costs and the longest system lifespans in the HVAC industry.
- Ductless mini-splits: A favorite for spaces lacking ductwork—such as sunrooms, garages, or older homes—mini-splits provide highly targeted comfort. Their modular nature enables precise zoning, allowing residents to only condition occupied rooms and fine-tune temperatures for personal preferences, ultimately saving energy.
Features now standard in modern systems, like variable-speed compressors, Wi-Fi-enabled thermostats, and advanced zoning controls, tie comfort and efficiency together. Consulting an HVAC expert for a tailored load calculation remains essential for any homeowner considering these options. The range of available heat pump designs ensures a solution for nearly every household scenario.
Energy Efficiency: Numbers That Matter
Heat pumps’ reputation for energy savings is well earned and supported by concrete data. In independent testing and field studies, replacing legacy electric resistance heating with a heat pump can lead to a drop in energy consumption by over 50%. According to The New York Times, as the grid decarbonizes, the efficiency edge of heat pumps grows further. During the summer, cooling with a high-SEER heat pump uses less electricity than older window units or central air conditioners.
Industry ratings such as SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) for cooling and HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor) for heating make it easier for consumers to compare models and make informed choices. High performance doesn’t just lead to savings. It also reduces the strain on power grids, which is especially critical during weather extremes. As more homes upgrade to heat pumps, the collective energy demand reduction offers communities an environmental win.
Installation And Maintenance Tips For Best Performance
Maximizing a heat pump’s performance starts with proper sizing and placement. An oversized unit can cycle too frequently, causing wear and wasted energy, while an undersized system may struggle on extreme days and increase energy consumption. Homeowners should insist on a detailed load calculation by an experienced HVAC technician, considering square footage, insulation, sun exposure, and other factors affecting thermal load.
Maintenance routines are equally vital. Air filters should be checked monthly and replaced when dirty to maintain good airflow and air quality. Outdoor units must remain free of debris and vegetation; regular coil cleaning keeps them running efficiently. Annual professional inspections—covering refrigerant levels, electrical components, and system controls—help catch wear-and-tear early and extend the system’s lifespan. Many companies offer affordable maintenance plans to make this process hassle-free.
Financial Incentives And Long-Term Savings
While investing in a modern heat pump system can feel daunting, many rebates and incentives exist to ease the cost. Local, state, and federal programs often provide upfront financial support, especially as part of climate policy or energy-saving initiatives. Homeowners may qualify for rebates from utility companies, tax credits, and even low-interest financing for qualified projects. These programs help shrink the gap between older equipment and next-generation systems, making upgrades more accessible for a broader range of households.
Lower utility bills help pay for the investment over time. Homeowners with heat pumps frequently report two-digit percentage drops in monthly power bills, with the initial outlay recovering within a few years. For those who pair a heat pump with other home upgrades—like attic insulation or solar power panels—the compounding effect is even greater. Staying organized and consulting the incentive program guidelines enables maximum savings.
Environmental Benefits Driving Change
Climate goals and local sustainability initiatives drive families and builders to think beyond savings. Using heat pump technology, households can lower their reliance on fossil fuels. Since heat pumps transfer heat instead of generating it from combustion, and as the electricity grid incorporates more renewables, the systems’ lifetime emissions are shrinking dramatically. Organizations and governments increasingly recommend heat pumps as a critical piece in reducing residential carbon output.
The compounding effect—lower operational energy, reduced grid demand, and compatibility with on-site solar—makes these systems attractive for those motivated by environmental stewardship. People who take this step often find peace of mind knowing they are helping drive bigger change, and that their home is ready for clean energy trends shaping the future.
Choosing The Right System For Your Home
Selecting a heat pump is a highly individualized process. Every home brings requirements based on layout, climate, insulation levels, and unique comfort expectations. A qualified HVAC professional remains the best resource for a thorough assessment. With expert guidance, a homeowner can choose a system built for their precise situation, optimizing efficiency, comfort, and long-term reliability.
Modern heat pumps are powering a quiet transformation in residential comfort and sustainability. Backed by robust data, compelling energy savings, and a growing array of user-friendly features, these systems have truly changed what’s possible for home heating and cooling. As more families experience the benefits firsthand, heat pumps are swiftly becoming the standard for comfort, value, and a healthier planet.
READ ALSO: What to Look for When Updating Key Areas